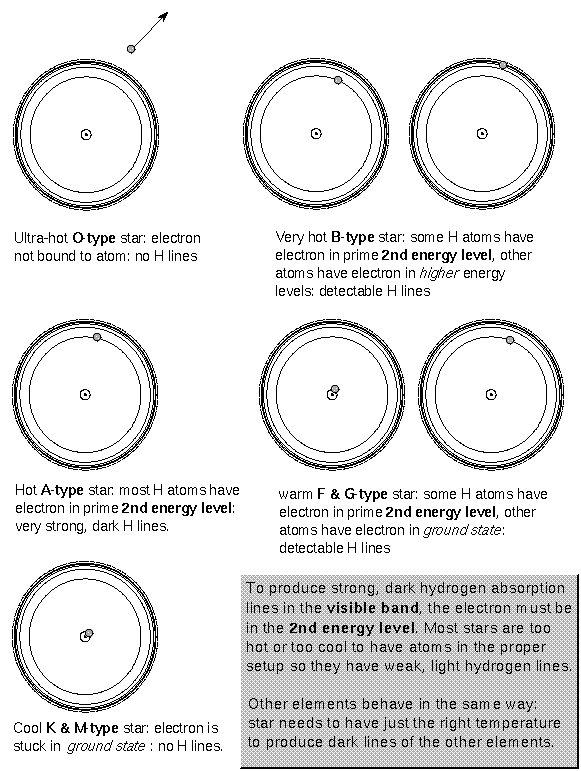
How hot is a star in F
Type A stars, which are hotter, are white in color and maintain temperatures of around 10,000 °C or 18,000 °F. The hottest of the types, B and O, are blue stars while the coolest of type M is red in color and have surface temperatures of about 3,000 °C or 5,400 °F.
What is the hottest star
WR 102
The hottest: WR 102
These stars not only burn incredibly hot and bright, but their stellar winds also blast much of their potential fuel into space. The hottest known star, WR 102, is one such Wolf-Rayet, sporting a surface temperature more than 35 times hotter than the Sun.
What is the hottest color star
Blue stars
Red stars are the coolest. Yellow stars are hotter than red stars. White stars are hotter than red and yellow. Blue stars are the hottest stars of all.
What are top 5 hottest stars
List
| Star name | Effective Temperature (K) | Spectral type |
|---|---|---|
| WR 102 | 210,000 | WO2 |
| WR 142 | 200,000 | WO2 |
| LMC195-1 | 200,000 | WO2 |
| BAT99-123 | 170,000 | WO3 |
How hot is a Type B star
10,000 K to 25,000 K
Class B stars typically range from 10,000 K to 25,000 K and are also bluish white but show neutral helium lines. The surface temperatures of A-type stars range from 7,400 K to about 10,000 K; lines of hydrogen are prominent, and these stars are white.
How hot is a dying star
Eventually, the outer layers of the star are carried away by a thick 31,000 mph (50,000 km/h) wind, leaving behind a hot core. This hot core has a surface temperature of about 90,000° Fahrenheit (50,000° Celsius) and is ejecting its outer layers in a much faster wind traveling 4 million mph (6 million km/h).
How hot is Sirius
It has a radius 1.71 times that of the Sun and a surface temperature of 9,940 kelvins (K), which is more than 4,000 K higher than that of the Sun.
Is Sirius hotter than the sun
The science of Sirius
That means it's a much hotter star than our sun; its surface temperature is about 17,000 degrees Fahrenheit (9,400 Celsius) in contrast to our sun's 10,000 degrees F (5,500 C).
Do purple stars exist
Green and purple stars do exist. The color of stars depends on their temperatures, and they emit radiation throughout the visible spectrum. But when a star emits peak radiation at a wavelength we define as green, it also emits radiation over the rest of the spectrum.
Are blue stars rare
They Are Quite Rare
Blue stars make up a tiny percentage of the stars we can see in our Milky Way galaxy. It takes a lot of energy to reach such a level, and most stars simply don't get there. We're just starting to look beyond our galaxy, but this pattern will likely continue in others as well.
Are F stars hotter than K stars
In order of decreasing temperature, O, B, A, F, G, K, and M. O and B are uncommon, very hot and bright. M stars are more common, cooler and dim.
How hot is a blue star
between 10,000 K and 50,000 K.
Red stars are cooler than the sun, with surface temperatures of 3,500 K for a bright red star and 2,500 K for a dark red star. The hottest stars are blue, with their surface temperatures falling anywhere between 10,000 K and 50,000 K.
How hot are G type stars
5,000–6,000 K.
stellar classification
The Sun is a class G star; these are yellow, with surface temperatures of 5,000–6,000 K. Class K stars are yellow to orange, at about 3,500–5,000 K, and M stars are red, at about 3,000 K, with titanium oxide prominent in their spectra.
How hot is a class G star
5,200 – 6,000
Stellar Classification
| Class | Temperature (°K) | Example Star |
|---|---|---|
| F | 6,000 – 7,500 | Procyon |
| G | 5,200 – 6,000 | The Sun |
| K | 3,700 – 5,200 | Pollux |
| M | < 3,700 | Betelgeuse |
How hot is a blue sun
Blue stars have estimated surface temperatures of 25,000 kelvin (K) (44,540 degrees F/ 24,726 degrees C), while red stars are much cooler at around 3,000 K (4,940 degrees F/ 2,726 degrees C), according to the University of Central Florida.
How hot is a black star
Dark stars are relatively cool — only around 10,000 kelvins (17,500 degrees Fahrenheit, 9,700 Celsius) — and would radiate at longer wavelengths than warmer objects.
How hot is a supernova
1,000,000,000 degrees Celsius
A supernova can light the sky up for weeks. The temperature in a supernova can reach 1,000,000,000 degrees Celsius.
How hot is Sirius K
It is a binary star in the constellation Canis Major. The bright component of the binary is a blue-white star 25.4 times as luminous as the Sun. It has a radius 1.71 times that of the Sun and a surface temperature of 9,940 kelvins (K), which is more than 4,000 K higher than that of the Sun.
Do rainbow stars exist
Stars come in many of the colours of the rainbow: blue, yellow, orange and red – as well as some stars that really are white. But there are no stars that look green!
Are pink stars real
In some galaxies, the pink color can dominate a telescope's entire field-of-view. This isn't some optical illusion or a false-color image; these regions and galaxies truly appear pink. At first glance, it's surprising, since there are no pink stars, and the majority of young starlight is preferentially blue.
What is the rarest star type
Each is classified as an O-type star — and O-type stars are the rarest main sequence stars in the universe, comprising just 0.00003% of known stars.
Are O or M stars hotter
Stars in the 'O' class are the most massive and hottest, stars in the 'M' class are the smallest and coolest. If you look closely at stars in the sky, you notice they are not all the same colour.
How hot is a red giant
4,000 to 5,800 degrees Fahrenheit
Because these stars' energy is spread across such a large area, their surface temperatures are actually relatively cool, reaching only 4,000 to 5,800 degrees Fahrenheit (2,200 to 3,200 degrees Celsius), a little over half as hot as the sun.
How hot are B type stars
10,000 K to 25,000 K
Class B stars typically range from 10,000 K to 25,000 K and are also bluish white but show neutral helium lines. The surface temperatures of A-type stars range from 7,400 K to about 10,000 K; lines of hydrogen are prominent, and these stars are white.…
How hot is an M star
2,400–3,700 K
Harvard spectral classification
| Class | Effective temperature | Fraction of all main-sequence stars |
|---|---|---|
| F | 6,000–7,500 K | 3.0% |
| G | 5,200–6,000 K | 7.6% |
| K | 3,700–5,200 K | 12% |
| M | 2,400–3,700 K | 76% |