How is space measured
So for cosmic distances, we switch to whole other types of units: astronomical units, light years and parsecs. Astronomical units, abbreviated AU, are a useful unit of measure within our solar system. One AU is the distance from the Sun to Earth's orbit, which is about 93 million miles (150 million kilometers).
What determines distance in space
System except pluto which we have not visited. It is also routinely used to measure the distance from the earth to the moon. Mirrors left by apollo astronauts reflect a laser being shot from earth and
Who determined how to measure distances in space
astronomer Friedrich Bessel
The first person to succeed at measuring the distance to a star using the parallax method was German astronomer Friedrich Bessel in 1838. Based on his observations, Bessel calculated that the star 61 Cygni, one of the stars in the Cygnus constellation, must be about 10 light-years away from Earth.
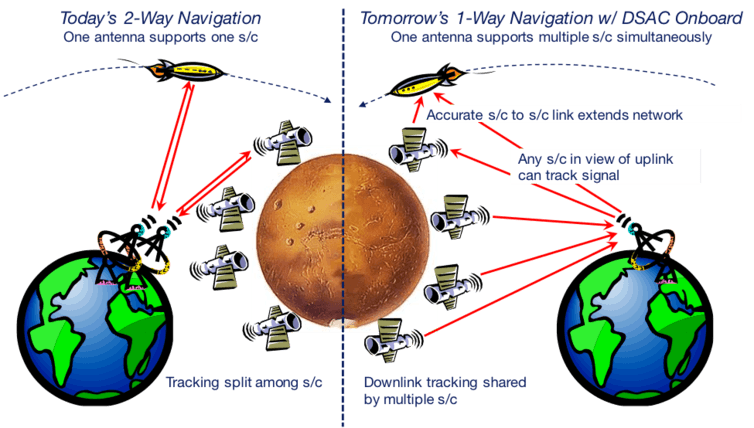
How are days measured in space
Fundamental to these precise measurements are atomic clocks. By measuring very stable and precise frequencies of light emitted by certain atoms (examples include hydrogen, cesium, rubidium and, for DSAC, mercury), an atomic clock can regulate the time kept by a more traditional mechanical (quartz crystal) clock.
How space is bigger
Why is the Universe so Big The Universe is so big because it is constantly expanding, and it does so at a speed that even exceeds the speed of light. Space itself is actually growing, and this is going on for around 14 billion years or so.
How does NASA measure mass in space
SLAMMD contains two springs which generate a known force (F) against the mass (m) of the astronaut. Optical sensors measure the acceleration (a) of the movement. Puttings these value for force and acceleration into the equation, SLAMMD outputs the astonaut's mass.
Is there a limit to how far we can see in space
We're looking back in time the further out we go because it takes time for light to travel to us. So the furthest out we can see is about 46.5 billion light years away, which is crazy, but it also means you can look back into the past and try to figure out how the universe formed, which again, is what cosmologists do.
Is there a limit to how far we can travel in space
There's no limit to how FAR we can go but there's still a finite number of galaxies that we could reach with close to the speed of light travel.
How did scientists decide to measure distances in space
By carefully measuring the angle through which the stars appear to move over the course of the year, and knowing how far Earth has moved, astronomers are able to use basic high-school geometry to calculate the star's distance.
How do they know how far away a galaxy is
Astronomers first measure the speed of the galaxy by analysing the shift in the galaxy's light towards the red end of its light spectrum (its 'redshift'), and once its speed is known, they can work out its distance.
Is 1 hour in space 7 years on Earth
The story is that 1 hour on that particular planet is equivalent to 7 years in space. Time dilation is real, but it's completely unrealistic that it would have an effect anywhere near that in any realistic scenario. In practice, it's a tiny fraction of a second, not many years.
How long is 1 minute in space
Explanation: The clocks in space tick more slowly than clocks on Earth., HENCE COVERING LESS TIME AS COMPARED TO EARTH IN THE SAME DURATION. Thus, upon calculation we find that one hour on Earth is equivalent to seven years in space. How long is 1 minute in space 186,000 miles * 60 seconds = 11,160,000 miles/minute.
Why is space infinite
Because space isn't curved they will never meet or drift away from each other. A flat universe could be infinite: imagine a 2D piece of paper that stretches out forever. But it could also be finite: imagine taking a piece of paper, making a cylinder and joining the ends to make a torus (doughnut) shape.
Why is space always growing
Although the expansion of the universe gradually slowed down as the matter in the universe pulled on itself via gravity, about 5 or 6 billion years after the Big Bang, according to NASA, a mysterious force now called dark energy began speeding up the expansion of the universe again, a phenomenon that continues today.
How do scientists know the mass of the universe
In general, by studying the dynamics of a large number of stars, the “behavior” of interstellar matter and dwarf galaxies which are located near the Milky Way and considered its satellites, scientists have determined that the total mass of our multistellar system within a radius of 130,000 light-years from its center …
How do scientists determine masses of things in space
To determine the mass of planets other than Earth, scientists need to study the tug of gravity between the planet and another object, such as a moon or star. Researchers can observe how something orbits another planet, or how that planet orbits a star, and use that information to estimate the mass of a planet.
Why can we see 46 billion light years away
The light that travels the longest gets stretched by the greatest amount, and the object that emitted that light is now at a greater distance because the universe is expanding. We can see objects up to 46.1 billion light-years away precisely because of the expanding universe.
How do they know the universe is 13.7 billion years old
We do not know the exact age of the universe, but we believe that it is around 13 billion years – give or take a few billion. Astronomers estimate the age of the universe in two ways: (a) by looking for the oldest stars; and (b) by measuring the rate of expansion of the universe and extrapolating back to the Big Bang.
How long would it take to travel 1 lightyear
This duration is a bit of a problem, as it makes space exploration a painstakingly slow process. Even if we hopped aboard the space shuttle discovery, which can travel 5 miles a second, it would take us about 37,200 years to go one light-year.
Where does space end
Practically, we cannot even imagine thinking of the end of space. It is a void where the multiverses lie. Our universe alone is expanding in every direction and covering billions of kilometres within seconds. There is infinite space where such universes roam and there is actually no end.
How do scientists know so much about space
The Great Observatories
NASA astronomers use several kinds of telescopes in space and on the ground. Each observes targets like stars, planets, and galaxies, but captures different wavelengths of light using various techniques to add to our understanding of these cosmic phenomenon.
How do scientists know what far away planets are made from
The most common method astronomers use to determine the composition of stars, planets, and other objects is spectroscopy. Today, this process uses instruments with a grating that spreads out the light from an object by wavelength. This spread-out light is called a spectrum.
How does NASA know how far away stars are
The Parallax Angle — How Astronomers Use Angular Measurement to Compute Distances in Space. The parallax angle is the angle between the Earth at one time of year, and the Earth six months later, as measured from a nearby star. Astronomers use this angle to find the distance from the Earth to that star.
How far away is the closest universe
Distance Information
The closest known galaxy to us is the Canis Major Dwarf Galaxy, at 236,000,000,000,000,000 km (25,000 light years) from the Sun. The Sagittarius Dwarf Elliptical Galaxy is the next closest , at 662,000,000,000,000,000 km (70,000 light years) from the Sun.
What happens every 176 years in space
A Once-in-a-Lifetime Alignment
Calculations reveal it is possible for a spacecraft launched in the late 1970s to visit all four giant outer planets, using the gravity of each planet to swing the spacecraft on to the next. This alignment occurs once every 176 years.