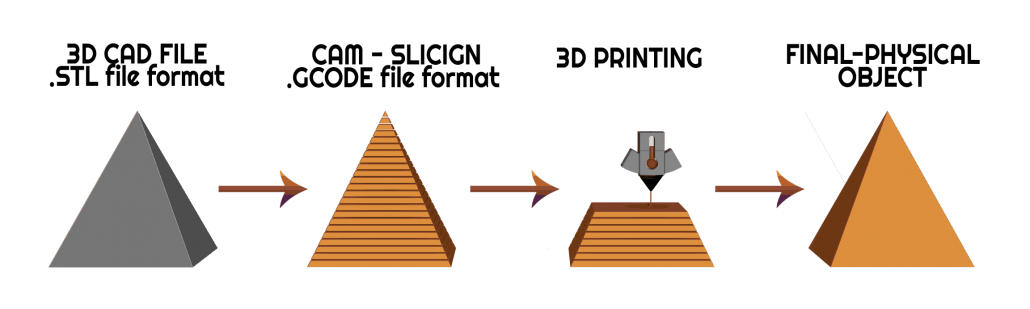
Is 3D printing a production process
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a method of creating a three dimensional object layer-by-layer using a computer created design. 3D printing is an additive process whereby layers of material are built up to create a 3D part.
What is a process called 3D printing
3D printing is a process in which a digital model is turned into a tangible, solid, three-dimensional object, usually by laying down many successive, thin layers of a material. 3D printing has become popular so quickly because it makes manufacturing accessible to more people than ever before.
Is 3D printing a fast process
Industrial 3D printers, with their large capacities and high production speeds can shave weeks or even months off the timeline for projects that require custom-built pieces when compared to hand-sculpting or other fabrication methods. But that doesn't mean every 3D printing job can be completed quickly.
What processes does 3D printing use
Processes
| Type | Technologies | Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Powder Bed | Selective laser sintering (SLS) | Thermoplastics, metal powders, ceramic powders |
| Direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) | Almost any metal alloy | |
| Laminated | Laminated object manufacturing (LOM) | Paper, metal foil, plastic film |
| Powder fed | Directed Energy Deposition (DED) | Almost any metal alloy |
What is the difference between 3D printing and manufacturing
In summary, the main difference between 3D printing and additive manufacturing is that 3D printing specifically involvesthe creation of objects by adding layersof material. Yet additive manufacturinginvolves the creation of objects by adding material, which may or may not come in layers.
Is 3D printing digital manufacturing
3D printing is one of the core group of digital manufacturing solutions that include Artificial Intelligence, the Internet of Things, and Robotics. Its rapidly accelerating growth is a key driver of what's called the fourth industrial revolution, also known as Industry 4.0.
What was the first 3D printing process called
The first process where three-dimensional material is deposited to form an object was done with material jetting or as it was originally called particle deposition.
Which 3D printing process is the most popular 3D printing process
Fused Deposition Modeling
Extrusion (also known as FDM for Fused Deposition Modeling or FFF for Fused Filament Fabrication) is the most common 3D printing technique.
Is 3D printing a slow process
While other methods of construction can take minutes to make a piece, the layer-by-layer method the 3d printers use makes them inherently slower due to the physical limitations inherent to the technology, both for Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) and for Resin-Based printers.
Is 3D printing really printing
In the 3D printing process, sequential layers of material are laid down by the '3D printer' until object creation is completed. 3D-printed objects are created through an additive process, where the printer places layer after layer of material until the desired thing is 'printed'.
What is the process of 3D printing plastic
Plastic 3D Printing Processes
Stereolithography (SLA) 3D printers use a laser to cure thermosetting liquid resins into hardened plastic in a process called photopolymerization. Selective laser sintering (SLS) 3D printers use a high-powered laser to fuse small particles of thermoplastic powder.
What is the most common 3D printing process
Fused deposition modeling (FDM), also known as fused filament fabrication (FFF), is the most widely used form of 3D printing at the consumer level, fueled by the emergence of hobbyist 3D printers.
Will 3D printing replace manufacturing
So, will 3D Printing Replace Traditional Manufacturing Well, considering the comparison we have done above, it would take decades for 3D printing to replace traditional manufacturing. In the near future; however, we can say that 3D printing could modify or improve some processes in the industry.
Why is 3D printing and additive manufacturing process
The term additive manufacturing refers to the process of adding material to an object. 3D printing is thus a type of additive manufacturing. It's called additive manufacturing when an object is made by adding material rather than subtracting it.
What industry does 3D printing fall under
Manufacturing. Most high-tech industries have taken advantage of 3D-printing manufacturing since the first patent for 3D printing in 1984, producing goods at an extraordinary speed, using less material, and reducing labor costs.
Who invented 3D printing process
Charles Hull
Charles Hull is the inventor of stereolithography, the first commercial rapid prototyping technology commonly known as 3D printing. The earliest applications were in research and development labs and tool rooms, but today 3D printing applications are seemingly endless.
Why is 3D printing weak
If the print head isn't hot enough, filament won't melt consistently, which can lead to under-extrusion and weak bonding between layers. A higher temperature will cause the filament to melt faster and result in a stronger filament flow through the nozzle.
What happens if you 3D print too fast
Travel speed indicates how fast the print head moves when not extruding filament. The travel speed can often be faster than the print speed without affecting quality. However, if it is too fast, it can lead to 3D printing defects like less precise prints or even layer shifts.
Why is 3D printing illegal
Printing items with a patent on them is illegal as you may face the possibility of being sued for 3D printing them. Since the items have patents on them, you are not licensed to reproduce them without approval from the owner.
How realistic is 3D printing
The accuracy is about ±0.3 mm. Metal powder fusion processes such as SLM use lasers to melt or sinter metal powder particles with an accuracy of about ± 0.1 mm. The type of 3D printing technology is not the only factor that determines the accuracy of 3D printing.
Is 3D printing just plastic
3D printing materials can vary widely, with options that include plastic, powders, resins, metal and carbon fiber. These materials make 3D printing a promising option for many parts, from highly accurate aerospace and industrial machinery components to customized consumer goods.
Is 3D printing always plastic
Although plastic is the most common material used in 3D printing, 3D printers can print materials other than plastic. Other materials that can be used in 3D printing include: Resin. Powder (polymers & metals)
Is 3D printing really the future
The development of new software has made 3D printing more accessible and user-friendly, allowing for easier design and preparation of parts for printing. Overall, the vision for materials in 3D printing in 2023 is one of increased diversity, performance, and sustainability.
Is 3D printing better than manufacturing
3D printing is much faster than many traditional manufacturing methods when producing small to medium objects. This speed improvement is because of the time needed to create the tooling for casts and molds used in traditional manufacturing. However, traditional manufacturing has more material options than 3D printing.
Is 3D printing considered additive manufacturing
3D printing and additive manufacturing are interchangeable, you need not worry about saying the wrong term because they both describe the same process.