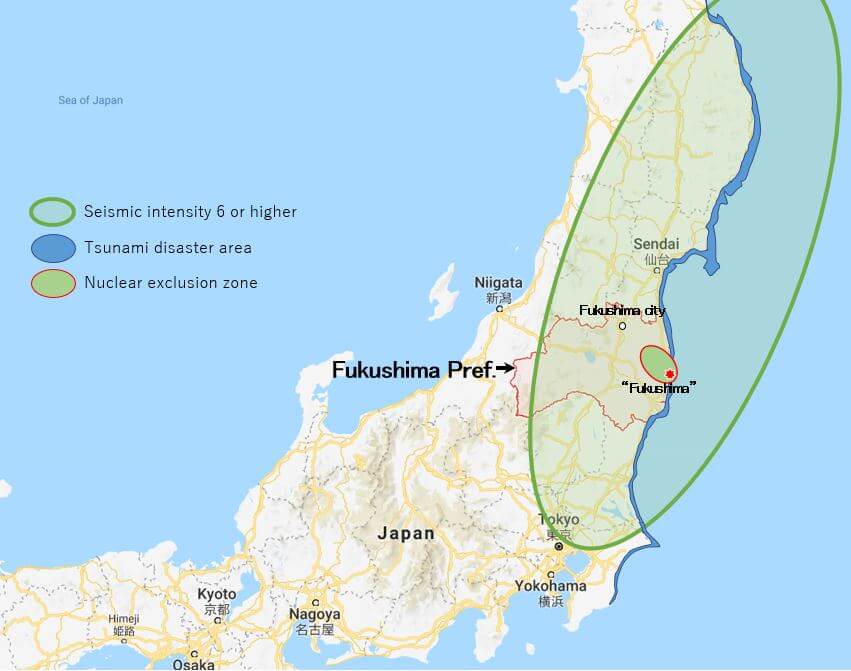
Is there a Fukushima exclusion zone
When this disaster struck Fukushima, reactors at a nuclear power plant overheated melted, causing radioactive materials to be released into the environment. Soon after the catastrophe, the Fukushima exclusion zone was created.
Can you go to Fukushima now
But is it safe to visit the area now The answer is yes. The radiation levels differ a bit depending on where you are, but overall the area is safe with normal levels of radiation.
Is Fukushima off limits
However, there are two large human-free zones that were made so intentionally—because of serious nuclear accidents. The areas around the sites of the Chernobyl and Fukushima disasters have been closed off and designated as nuclear exclusion zones because of the ongoing dangers of radiation and its effects.
What is the danger zone for Fukushima
A nuclear emergency was declared by the government of Japan on 11 March. Later Prime Minister Naoto Kan issued instructions that people within a 20 km (12 mi) zone around the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant must leave, and urged that those living between 20 km and 30 km from the site to stay indoors.
Is it safe to travel to Japan after Fukushima
Restricted areas exist around the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear power plant. The 2011 earthquake caused the release of lethal radiation. Radiation levels in most parts of Japan, including Tokyo, are within the normal range. Monitor advice by the Japanese Government.
Was Chernobyl worse than Fukushima
The accident at Fukushima occurred after a series of tsunami waves struck the facility and disabled systems needed to cool the nuclear fuel. The accident at Chernobyl stemmed from a flawed reactor design and human error. It released about 10 times the radiation that was released after the Fukushima accident.
Could something like Fukushima happen again
A 2015 study from European researchers estimated that there was a 50% chance of another Fukushima-scale nuclear accident within the next 50 years, a Chernobyl-scale event in the next 27 years, or a Three Mile Island-scale event in the next 10 years.
Has Fukushima been cleaned up
Most of the radioactive debris blasted by the hydrogen explosions has been cleared and the torn buildings have been fixed.
Can Fukushima happen again
A 2015 study from European researchers estimated that there was a 50% chance of another Fukushima-scale nuclear accident within the next 50 years, a Chernobyl-scale event in the next 27 years, or a Three Mile Island-scale event in the next 10 years.
Is Fukushima a difficult to return zone
Difficult-to-return zone
This means this area hasn't been affected by the Tsunami disaster. The Japanese government decided to make it a difficult-to-return zone but they haven't done enough nuclear decontamination in this area. So radiation is much higher than other areas.
Is it safe to visit Tokyo after Fukushima
Even permanent residents of the prefecture where the meltdown occurred do not appeared to be harmed by radiation. And all of Japan's major tourist destinations – Tokyo, Kyoto, Osaka, Nagoya, Hiroshima, Kobe, Hokkaido and Okinawa – are more than 150mi away from the exclusion zone.
What was the 2 worst nuclear disaster in history
The Fukushima accident was an accident in 2011 at the Fukushima Daiichi (“Number One”) nuclear power plant in Japan. It is the second worst nuclear accident in the history of nuclear power generation, behind the Chernobyl disaster.
Is Chernobyl level 7
To date, the nuclear accidents at the Chernobyl (1986) and Fukushima Daiichi (2011) nuclear power plants, are the only INES level 7 nuclear accidents.
Is Fukushima still hot
The radioactive detritus at Fukushima is still throwing off roughly one million watts worth of heat, according to Fairewinds Energy, a nuclear safety advocacy group based in Burlington, Vt. That heat turns water into steam—and when the air is cold enough, as it is in winter in Japan, that steam is visible.
Is Fukushima worse than Chernobyl
The Fukushima event has been rated 7 on the International Nuclear and Radiological Event Scale, the same level as the 1986 Chernobyl accident. Even so, Japanese authorities estimate that radiation released at Fukushima is only 10 percent of the amount released from the Ukrainian plant.
Is Fukushima back to normal
Ten years after the disaster, life has returned pretty much to normal in many parts of Fukushima Prefecture. In some of the inland cities such as Fukushima city or Koriyama, there are few if any visible signs that the nuclear accident ever occurred.
How long until Fukushima is no longer radioactive
Past and Present contamination
These areas still have relatively high radioactivity. The half-life of radiocesium is about 29 years, meaning the quantity of the radioactive material should drop by half by roughly 2041.
How long will the Fukushima exclusion zone last
Past and Present contamination
These areas still have relatively high radioactivity. The half-life of radiocesium is about 29 years, meaning the quantity of the radioactive material should drop by half by roughly 2041.
Is Japan safe to travel after Fukushima
Restricted zones exist around the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear power plant. The 2011 earthquake caused the release of lethal radiation. Radiation levels in most parts of Japan, including Tokyo, are within the normal range. Medical facilities are of a high standard.
Is food from Japan safe after Fukushima
Is it safe to eat foods from Fukushima Yes, it's safe. To ensure the safety of foods produced in Fukushima Prefecture, Japan conducts multi-layer examinations for radioactive substances at each phase of production and distribution and publicizes the results. The safety of these foods is evaluated highly by the FAO.
How long will Fukushima be radioactive
Past and Present contamination
These areas still have relatively high radioactivity. The half-life of radiocesium is about 29 years, meaning the quantity of the radioactive material should drop by half by roughly 2041.
Why wasn t Fukushima as bad as Chernobyl
Notably, the reactor designs are completely different and to date, the public health consequences at Fukushima are much less severe. Although some damage to the uranium fuel is expected at Fukushima Daiichi, there have not been releases of radiation into the atmosphere at the levels seen during the Chernobyl accident.
Why is Fukushima safer than Chernobyl
According to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), there was less total atmospheric release of radioactivity from the Fukushima accident compared with Chernobyl due to the different accident scenarios and mechanisms of radioactive releases.
Is Fukushima still being cleaned
The Fukushima disaster cleanup is an ongoing attempt to limit radioactive contamination from the three nuclear reactors involved in the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster that followed the earthquake and tsunami on 11 March 2011.
Why Fukushima is not that bad
– Radiation in most of the Evacuation Zone around Fukushima is low enough for people to move back. Except for a relatively small region around the reactors, the risk of evacuees moving back to their homes are the same as driving a car (UNSCEAR).