What is the difference between traditional manufacturing and 3D printing
3D printing prints an object layer-by-layer as opposed to subtractive processes—like many traditional manufacturing processes—in which the product is cut out of a larger block of material. As a result, 3D printing creates less material waste.
What is the difference between machining and 3D printing
The main difference between CNC machining and 3D printing is in the nature of the technology: while CNC machining subtracts material from a billet to form a net shape part, 3D printing adds material, layer by layer.
What is the difference between additive manufacturing and 3D printing and rapid prototyping
The term rapid prototyping is different from 3D printing/additive manufacturing. Rapid prototyping is the technique of fabricating a prototype model from a CAD file. In other words, 3D printing/additive manufacturing is the process, and rapid prototyping is the end result.
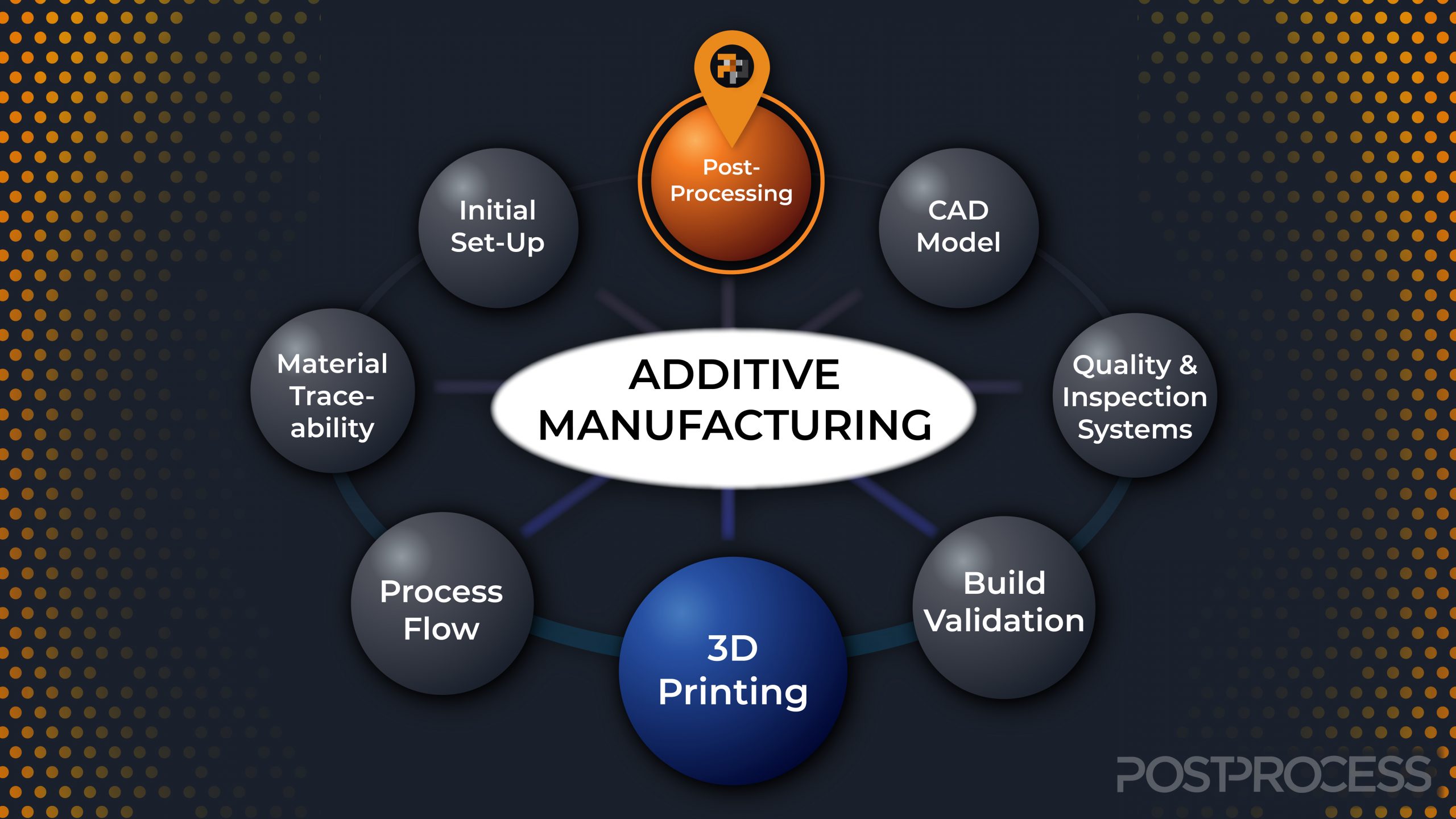
What is the 3D printing or additive manufacturing process
Three-dimensional (3D) printing is an additive manufacturing process that creates a physical object from a digital design. The process works by laying down thin layers of material in the form of liquid or powdered plastic, metal or cement, and then fusing the layers together.
Is 3D printing considered manufacturing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has come a long way since it was first developed in the 1980s. While 3D printing originated as a tool for rapid prototyping, it has now evolved to cover a number of different technologies.
What are two advantages that 3D printing has over traditional manufacturing
Traditional manufacturing processes require complex tooling. 3D printing eliminates the need to build molds and other tooling before production. The flexibility of 3D printing processes allows multiple SKUs to be produced on a single 3D printing manufacturing line.
Is 3D printing part of manufacturing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has come a long way since it was first developed in the 1980s. While 3D printing originated as a tool for rapid prototyping, it has now evolved to cover a number of different technologies.
Can 3D printing replace manufacturing
So, will 3D Printing Replace Traditional Manufacturing Well, considering the comparison we have done above, it would take decades for 3D printing to replace traditional manufacturing. In the near future; however, we can say that 3D printing could modify or improve some processes in the industry.
What is the difference between additive manufacturing and manufacturing
Additive manufacturing processes build objects by adding material layer by layer, while subtractive manufacturing removes material to create parts.
What are the advantages of 3D printing compared to other manufacturing techniques
Traditional manufacturing processes require complex tooling. 3D printing eliminates the need to build molds and other tooling before production. The flexibility of 3D printing processes allows multiple SKUs to be produced on a single 3D printing manufacturing line.
Why is 3D printing the future of manufacturing
3D printing can produce parts, allow for changes without requiring extra tools or equipment in comparison to other methods. The future possibilities are exponential and this is why the world is fixated on the technology. 3D printing turns the head on standard manufacturing.
Will 3D printing replace manufacturing
So, will 3D Printing Replace Traditional Manufacturing Well, considering the comparison we have done above, it would take decades for 3D printing to replace traditional manufacturing. In the near future; however, we can say that 3D printing could modify or improve some processes in the industry.
Why is 3D printing cheaper than manufacturing
3D printing does not incur additional costs with each new unit produced. This means it can produce one part and hundreds of parts at almost the same cost per part. This is impossible with traditional manufacturing, which often requires an expensive tooling stage that is only justified if products are mass-produced.
What are the 5 differences between manufacturing and services
There are five main differences between service and manufacturing organizations: the tangibility of their output; production on demand or for inventory; customer-specific production; labor-intensive or automated operations; and the need for a physical production location.
Is 3D printing the only type of additive manufacturing
The term 3D printing is typically used to refer to all types of additive manufacturing. However, this is not quite accurate. Strictly speaking, 3D printing refers only to the transformation of a digital CAD (Computer-Aided Design) file into a three-dimensional physical solid object or part.
Why should we consider using 3D printing over traditional manufacturing
3D printing can produce a part in a matter of hours, while traditional manufacturing methods such as injection molding and machining can take days or even weeks to produce a part. This is because 3D printing does not require the creation of molds or tooling, which can be time-consuming to design and manufacture.
How does 3D printing produce less compared to other manufacturing processes
Material Waste
Even still, the waste generated by 3D printing is on average 70-90% less than waste generated by subtractive manufacturing methods.
What are the advantages of 3D printing over traditional manufacturing
Traditional manufacturing processes require complex tooling. 3D printing eliminates the need to build molds and other tooling before production. The flexibility of 3D printing processes allows multiple SKUs to be produced on a single 3D printing manufacturing line.
What are the main differences between manufacturing and services
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN MANUFACTURING AND SERVICE ORGANIZATIONS
First, manufacturing organizations produce physical, tangible goods that can be stored in inventory before they are needed. By contrast, service organizations produce intangible products that cannot be produced ahead of time.
Is there any difference between manufacturing and industry
In general, manufacturers have a standardized way of producing goods. Goods are produced en masse in a factory or warehouse-type environment. One finished product is generally the same as the next. Service Industries include those industries that do not produce goods and instead provide services.
Will 3D printing replace traditional manufacturing
So, will 3D Printing Replace Traditional Manufacturing Well, considering the comparison we have done above, it would take decades for 3D printing to replace traditional manufacturing. In the near future; however, we can say that 3D printing could modify or improve some processes in the industry.
What are the main advantages of 3D printing compared to traditional manufacturing techniques
What are the Pros of 3D PrintingFlexible Design. 3D printing allows for the design and print of more complex designs than traditional manufacturing processes.Rapid Prototyping.Print on Demand.Strong and Lightweight Parts.Fast Design and Production.Minimising Waste.Cost Effective.Ease of Access.
What is the difference between production and manufacturing
Definition: While Production converts inputs or intermediates to a final output or services, which may or may not use machinery, Manufacturing is the process of transforming raw materials into finished goods, by deploying various sequential processes, labour, and machinery.
What is the main difference between manufacturing and production
Manufacturing is the process where machines produce goods from raw materials. Production is the process of converting resources into finished products. Manufacturing includes producing goods that can be immediately sold off and are suitable for use.
What are the advantages of additive manufacturing or 3D printing
10 benefits of Additive ManufacturingLower start-up costs. Manufacturing start-up costs can be high.Easy to learn (and use)Reduced raw material wastage.Customisation to the individual.Digital design integration.Speed of first prototype.Speed from prototype to production.Lower energy and environmental costs.