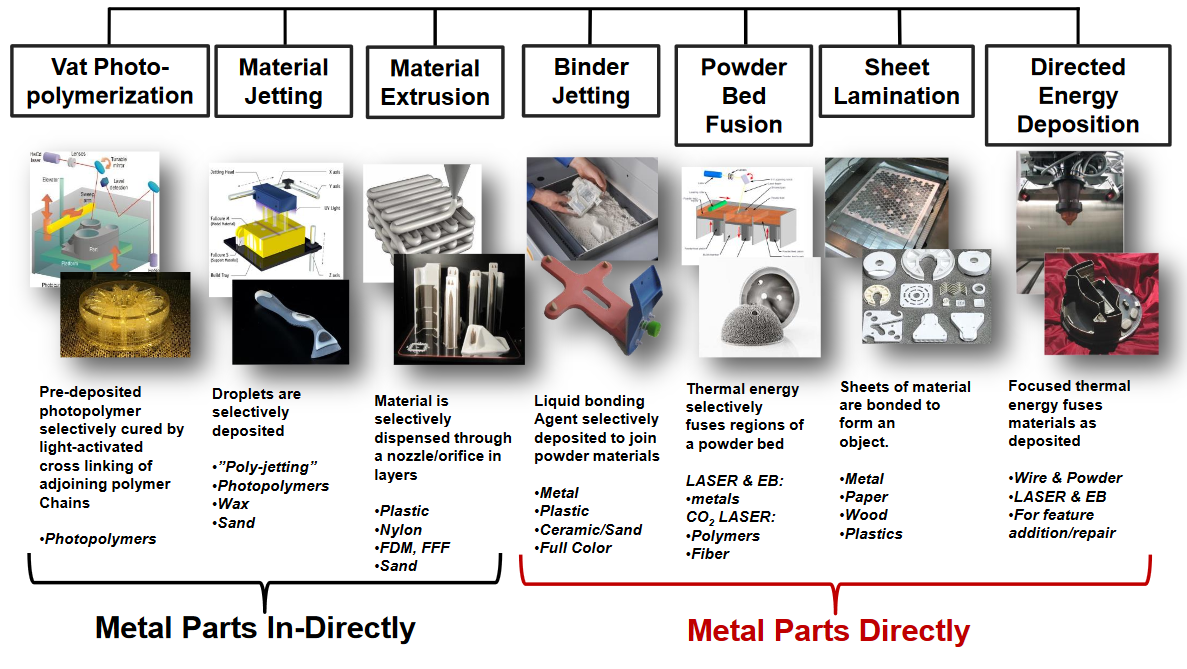
What type of manufacturing process is 3D printing
3D printing is an additive process whereby layers of material are built up to create a 3D part. This is the opposite of subtractive manufacturing processes, where a final design is cut from a larger block of material. As a result, 3D printing creates less material wastage.
Is 3D printing considered manufacturing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has come a long way since it was first developed in the 1980s. While 3D printing originated as a tool for rapid prototyping, it has now evolved to cover a number of different technologies.
Is 3D printing an additive manufacturing process
The term 3D printing is typically used to refer to all types of additive manufacturing.
What is a process called 3D printing
3D printing is a process in which a digital model is turned into a tangible, solid, three-dimensional object, usually by laying down many successive, thin layers of a material. 3D printing has become popular so quickly because it makes manufacturing accessible to more people than ever before.
Is 3D printing subtractive manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, often referred to as 3D printing, adds successive layers of material to create an object. Subtractive manufacturing removes material to create an object.
Is 3D printing smart manufacturing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a rapidly growing technology that has changed the way companies design, prototype and produce products. Smart factories primarily use 3D printing to manufacture complex parts and components quickly and precisely.
What industry does 3D printing fall under
Manufacturing. Most high-tech industries have taken advantage of 3D-printing manufacturing since the first patent for 3D printing in 1984, producing goods at an extraordinary speed, using less material, and reducing labor costs.
Is 3D printing additive or subtractive manufacturing
The differences between additive manufacturing and subtractive manufacturing are significant. Additive manufacturing, often referred to as 3D printing, adds successive layers of material to create an object. Subtractive manufacturing removes material to create an object.
Is 3D printing a method of subtractive manufacturing
In contrast to the subtractive process of removing material from a larger piece, additive manufacturing or 3D printing processes build objects by adding material one layer at a time, with each successive layer bonding to the preceding layer until the part is complete.
Which of the following processes does 3D printing use
The creation of a 3D printed object is achieved using additive processes. In an additive process an object is created by laying down successive layers of material until the object is created. Each of these layers can be seen as a thinly sliced cross-section of the object.
Is 3D printing a long process
This can vary from as little as 30 minutes to several days. The bigger the part and the greater the complexity, the longer it takes to print. However, a simpler and smaller item can be printed much faster.
What is an example of a subtractive manufacturing process
Lathe-turning, milling, drilling, sawing, thread-cutting and gear-cutting are some examples of subtractive processes involving metal-cutting that are traditionally carried out in specialized machines.
Is additive manufacturing smart manufacturing
Additive manufacturing (AM) is a smart manufacturing technique that fabricates components directly from 3-D models by selectively joining materials.
What is the difference between 3D printing and manufacturing
In summary, the main difference between 3D printing and additive manufacturing is that 3D printing specifically involvesthe creation of objects by adding layersof material. Yet additive manufacturinginvolves the creation of objects by adding material, which may or may not come in layers.
What is the industrial production name for 3D printing
additive manufacturing
3D printing is a synonym for additive manufacturing, they are two terms for the same process which both mean the same thing. However, 'additive manufacturing' is generally the term used by industry.
What are the manufacturing uses of 3D printing
3D printing is used to manufacture moulds for making jewelry, and even the jewelry itself. 3D printing is becoming popular in the customisable gifts industry, with products such as personalized models of art and dolls, in many shapes: in metal or plastic, or as consumable art, such as 3D printed chocolate.
Can 3D printing be subtractive
Meanwhile, 3D printing is currently mainly used to complement subtractive manufacturing methods. However, as the name suggests, unlike additive manufacturing, these techniques consist of removing material to produce a part of the desired size.
Are 3D printing and additive manufacturing synonyms
Between the terms 3D printing and additive manufacturing, there is no difference. 3D printing and additive manufacturing are synonyms for the same process. Both terms reference the process of building parts by joining material layer by layer from a CAD file.
What is the most common process used by 3D printers
Moreover, plastic material for 3D printing is cost-effective compared to other materials. The most common 3D printing method that uses plastic material is fused deposition modeling (FDM). In FDM 3D printing, thermoplastic filaments are melted and shaped one layer at a time.
What is the process of 3D printing plastic
Plastic 3D Printing Processes
Stereolithography (SLA) 3D printers use a laser to cure thermosetting liquid resins into hardened plastic in a process called photopolymerization. Selective laser sintering (SLS) 3D printers use a high-powered laser to fuse small particles of thermoplastic powder.
What is the most common 3D printing process
Fused deposition modeling (FDM), also known as fused filament fabrication (FFF), is the most widely used form of 3D printing at the consumer level, fueled by the emergence of hobbyist 3D printers.
Why does the 3D printing process take so long to accomplish
It is all about precision
Consequently, the larger and more complex the object, the more time will be needed to print it. 3D printing is a very precise method, which also makes the process longer. After all we want the printed models to be exact representations.
Is 3D printing additive or subtractive
Additive manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, often referred to as 3D printing, adds successive layers of material to create an object. Subtractive manufacturing removes material to create an object.
Is subtractive manufacturing 3D printing
In contrast to the subtractive process of removing material from a larger piece, additive manufacturing or 3D printing processes build objects by adding material one layer at a time, with each successive layer bonding to the preceding layer until the part is complete.
Is additive manufacturing advanced manufacturing
Advanced manufacturing is a broad term that refers to the use of innovative technologies and processes to improve the efficiency and productivity of manufacturing. Advanced manufacturing encompasses various techniques, including automation, additive manufacturing, and robotics.