What scale of measurement is 1 10
ordinal variable
An ordinal variable, is one where the order matters but not the difference between values. For example, you might ask patients to express the amount of pain they are feeling on a scale of 1 to 10.
What type of data is a scale
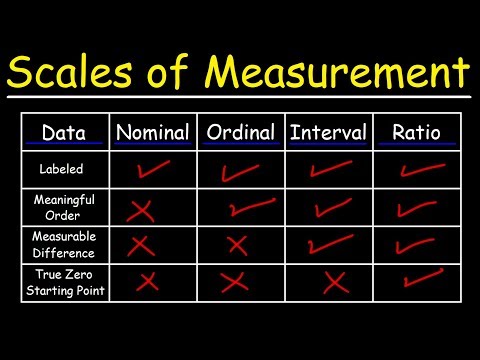
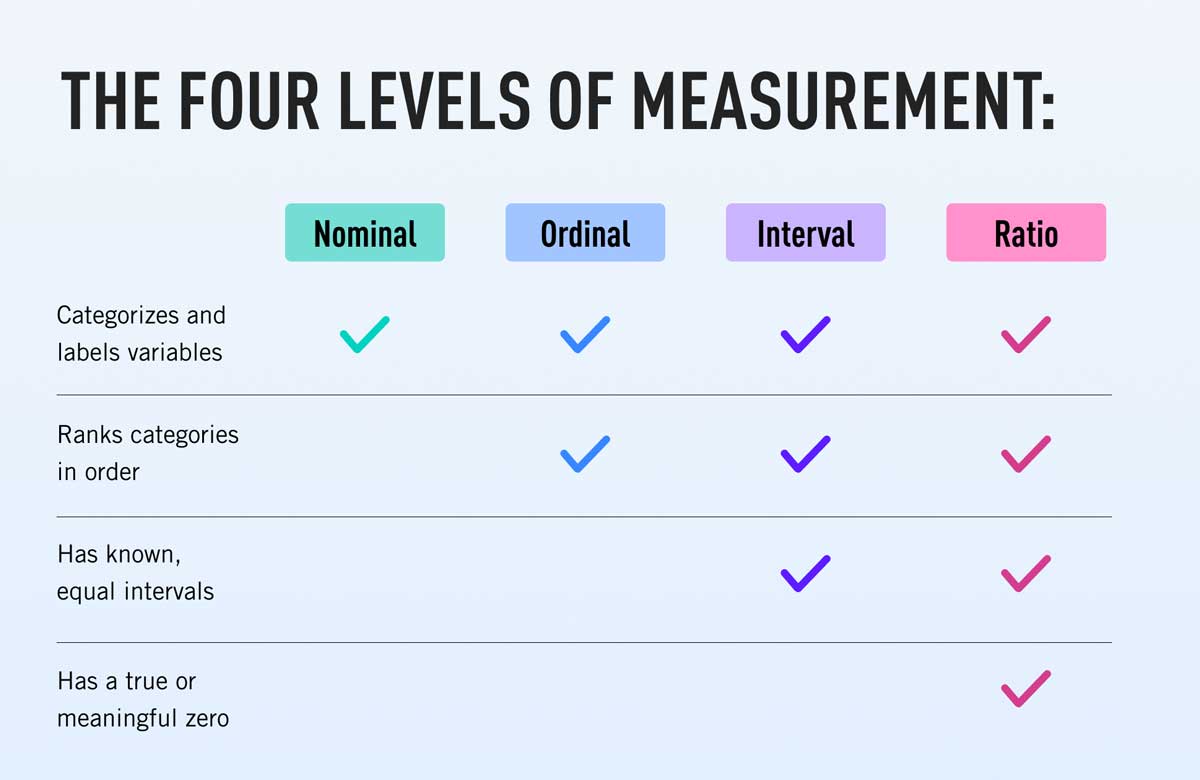
In statistics, there are four data measurement scales: nominal, ordinal, interval and ratio. These are simply ways to sub-categorize different types of data (here's an overview of statistical data types) .
Is scale data nominal or ordinal
Nominal scale is a naming scale, where variables are simply “named” or labeled, with no specific order. Ordinal scale has all its variables in a specific order, beyond just naming them.
What type of data is a scale of 1 5
Ordinal Scale: All the data points from the ordered set falls in this category. Ex: Ratings on a 1–5 scale (5 being highest and 1 being lowest).
Is on a scale from 1 to 10 quantitative data
Data from Likert scales and continuous (e.g. 1-10) rating scales are quantitative. These scales assume equal intervals between points.
What does 10 1 measurement mean
This standard stated that when parts were being measured that the accuracy tolerances of the measuring equipment should not exceed 10% of the tolerances of the parts being checked. This rule is often called the 10:1 rule or the Gagemaker's Rule.
Is scale a ordinal
Ordinal scale is the 2nd level of measurement that reports the ranking and ordering of the data without actually establishing the degree of variation between them. Ordinal level of measurement is the second of the four measurement scales. “Ordinal” indicates “order”.
Is a scale an ordinal variable
Ordinal is categorical with ranking where as scale is quantitative.
Is A scale nominal
A nominal scale is the 1st level of measurement scale in which the numbers serve as “tags” or “labels” to classify or identify the objects. A nominal scale usually deals with the non-numeric variables or the numbers that do not have any value. A nominal scale variable is classified into two or more categories.
Is scale of 1 to 5 quantitative
Interval scales – These scales have answer sets where each interval within it tells you about a deeper meaning, rather than just an ordered grouping. It provides quantitative data. For example, 1-5 is an ordered list of numbers that occur one after the other.
Is a scale of 1 to 5 categorical
Opinion variables on a 1 to 5 or 1 to 10 scale are usually considered as ordinal categorical variables.
Is a 1 to 10 scale qualitative or quantitative
Rating scales do not produce qualitative data, irrespective of what the end-point labels may be. Data from Likert scales and continuous (e.g. 1-10) rating scales are quantitative. These scales assume equal intervals between points.
Is a scale 1 10 a discrete variable
These people will rate this new product and an old product in the same category and rate the products on a scale, typically on a scale of 1-10. In this case, the score given by each taster for each of the products is a discrete variable.
What is a measurement based on 10
The metric system is a base 10 system. This means that each successive unit is 10 times larger than the previous one. The names of metric units are formed by adding a prefix to the basic unit of measurement.
What is 10 rule measurement
The Rule of 10 says that a measurement tool should have 10 times more resolution than the tolerance of the dimension. So, if you need to measure a part whose tolerance is expressed in hundredths of an inch (0.01"), you should select a measurement system whose resolution is expressed in thousandths of an inch (0.001").
Is a number scale ordinal or interval
The interval level is a numerical level of measurement which, like the ordinal scale, places variables in order. Unlike the ordinal scale, however, the interval scale has a known and equal distance between each value on the scale (imagine the points on a thermometer).
Is a 1 5 scale ordinal
1 indicates extremely unsatisfactory, 2 is unsatisfactory, 3 is neutral, 4 is satisfactory and 5 indicates extremely satisfactory. Here, the data collected will be on an ordinal scale as there is a rank associated with each of the answer options, i.e. 2 is lower than 4 and 4 is lower than 5.
Is a scale an interval variable
An interval scale is one where there is order and the difference between two values is meaningful. Examples of interval variables include: temperature (Farenheit), temperature (Celcius), pH, SAT score (200-800), credit score (300-850).
What type of variables are scales
Four Types of Variables
You can see there are four different types of measurement scales (nominal, ordinal, interval and ratio). Each of the four scales, respectively, typically provides more information about the variables being measured than those preceding it.
Is a 1 5 scale nominal
The ordinal level of measurement groups variables into categories, just like the nominal scale, but also conveys the order of the variables. For example, rating how much pain you're in on a scale of 1-5, or categorizing your income as high, medium, or low.
What is ordinal scale data
The Ordinal scale includes statistical data type where variables are in order or rank but without a degree of difference between categories. The ordinal scale contains qualitative data; 'ordinal' meaning 'order'. It places variables in order/rank, only permitting to measure the value as higher or lower in scale.
Is a scale from 1 10 quantitative
Data from Likert scales and continuous (e.g. 1-10) rating scales are quantitative. These scales assume equal intervals between points.
Is a scale of 1 10 categorical
Opinion variables on a 1 to 5 or 1 to 10 scale are usually considered as ordinal categorical variables.
Is a scale of 1 10 discrete or continuous
These people will rate this new product and an old product in the same category and rate the products on a scale, typically on a scale of 1-10. In this case, the score given by each taster for each of the products is a discrete variable.
Are scales qualitative or quantitative
Some researchers call the first two scales of measurement (Ratio Scale and Interval Scale) “quantitative” because they measure things numerically, and call the last scale of measurement (Nominal Scale) “qualitative” because you count the number of things that have that quality.