Who controls the US nuclear weapons
The U.S. President
The U.S. President has sole authority to authorize the use of U.S. nuclear weapons. This authority is inherent in his constitutional role as Commander in Chief.
Who maintains the US nuclear arsenal
the Department of Energy
NNSA, a part of the Department of Energy, manages the nuclear warheads and bombs, as well as the infrastructure and capabilities needed to produce and maintain these weapons.
Who has the largest nuclear arsenal in the world
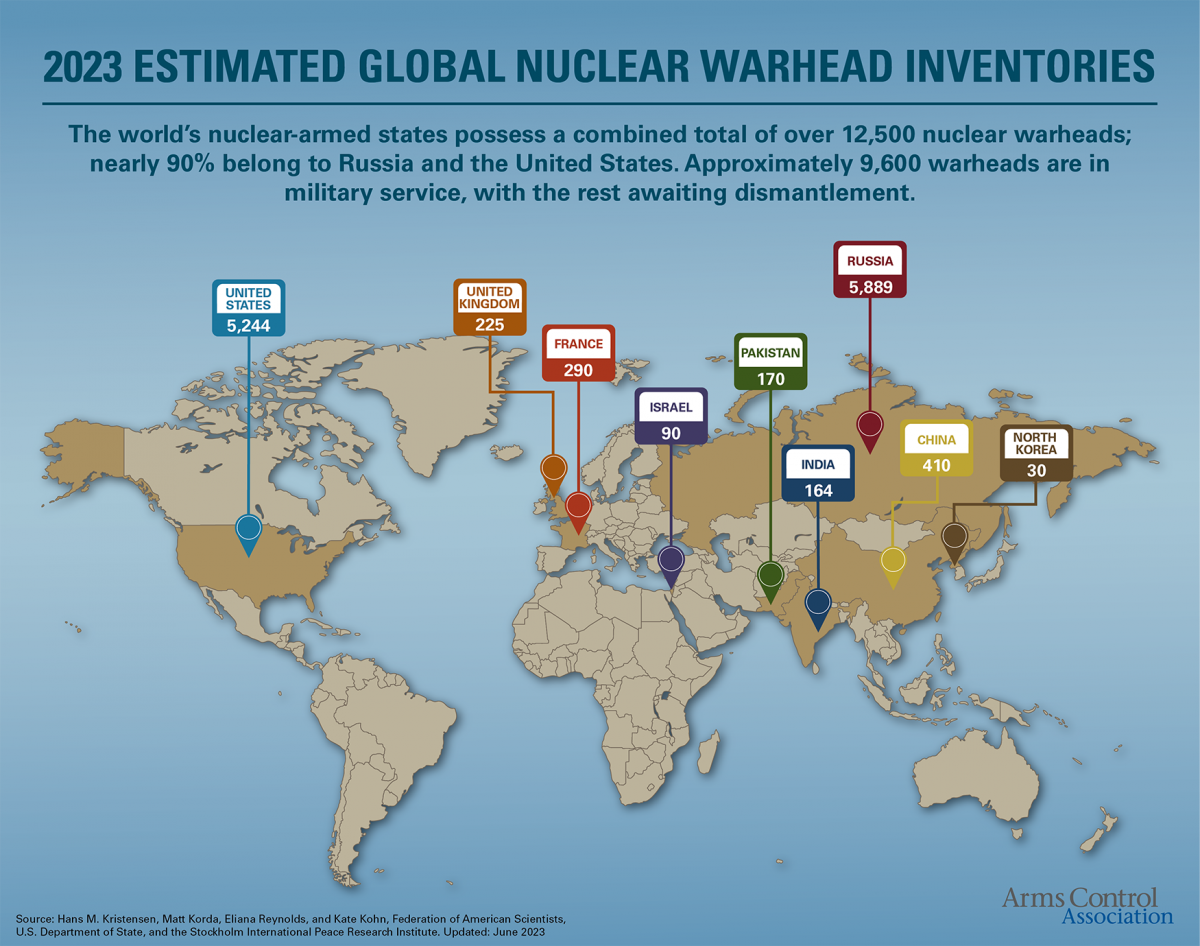
Countries' Nuclear Arsenals from Largest to SmallestRussia (5,977 warheads)United States (5,428)China (350)France (290)United Kingdom (225)Pakistan (165)India (160)Israel (90)
Which country has the most powerful weapons in the world
Who has the most nuclear weapons Russia has the most confirmed nuclear weapons, with 5,997 nuclear warheads. The United States follows behind with 5,428 nuclear weapons, hosted in the US and 5 other nations: Turkey, Italy, Belgium, Germany and the Netherlands.
How did China get nukes
In 1951, China signed a secret agreement with Moscow through which China provided uranium ores in exchange for Soviet assistance in nuclear technology. China began developing nuclear weapons in the late 1950s with substantial Soviet assistance.
Who is the leader of nuclear defense
Acting Chief and Associate Administrator for Defense Nuclear Security. David Hoagland is NNSA's Acting Chief and Associate Administrator for Defense Nuclear Security, a position he has held since March 2023.
Who is in charge of nuclear missiles
Command and control
Since World War II, the President of the United States has had sole authority to launch U.S. nuclear weapons, whether as a first strike or nuclear retaliation.
Who guards US nuclear power plants
The NRC holds nuclear plants to the highest security standards of any industry, and every plant exceeds those standards. The U.S. Department of Homeland Security agrees. Nuclear power plants continue to be among the best-protected private sector facilities in the nation.
What country owns the strongest nuke
Russia's Tsar bomba: World's most powerful nuclear weapon of mass destruction.
Does Russia still have Tsar Bomba
As only one bomb was built to completion, that capability has never been demonstrated. The remaining bomb casings are located at the Russian Atomic Weapon Museum in Sarov and the Museum of Nuclear Weapons, All-Russian Scientific Research Institute Of Technical Physics, in Snezhinsk.
Which is the No 1 weapons in the world
Of course, nuclear weapons surpass all other weapons made to date, because they have enormous destructive power and can cut down an entire city and a large part of the population, and radiation after a nuclear attack would be present for decades.
Which is the deadliest weapon on Earth
> Lethality index score: 210,000,000,000
Created in the manic arms race of the Cold War, the B-41 hydrogen bomb is the deadliest weapon on this list. The bomb has never been used in warfare but is capable of destruction on a colossal scale.
Why doesn t China have a lot of nukes
From a production standpoint, China probably does not have enough fissile material to produce 3,000 nuclear weapons. Such an arsenal would require 9–12 tons of plutonium as well as 45–75 tons of enriched uranium and a substantial amount of tritium.
Who invented the nuke
J. Robert Oppenheimer
J. Robert Oppenheimer (1904-1967) was an American theoretical physicist. During the Manhattan Project, Oppenheimer was director of the Los Alamos Laboratory and responsible for the research and design of an atomic bomb. He is often known as the “father of the atomic bomb.”
Who is the nuclear watchdog
IAEA
International Atomic Energy Agency
| Abbreviation | IAEA |
|---|---|
| Formation | 29 July 1957 |
| Type | International organization |
| Legal status | Active |
| Headquarters | Vienna, Austria |
Who runs the nuclear power
The NRC regulates commercial nuclear power plants and other uses of nuclear materials, such as in nuclear medicine, through licensing, inspection and enforcement of its requirements.
Who is the owner of nuclear bomb
Nine countries possess nuclear weapons: the United States, Russia, France, China, the United Kingdom, Pakistan, India, Israel, and North Korea. In total, the global nuclear stockpile is close to 13,000 weapons.
Is the Department of Energy responsible for nuclear weapons
The DOE/NNSA has federal responsibility for the design, testing and production of all nuclear weapons.
Which bomb can destroy whole world
Russia's Tsar bomba: World's most powerful nuclear weapon of mass destruction. The Tsar bomba exploded about 4 km above the ground and reportedly produced a mushroom cloud 60 km high.
Could the Tsar Bomba destroy New York
If such a weapon exploded in a large American city such as New York, Chicago, San Francisco, or Washington, D.C., their metropolitan areas plus large portions of their surrounding suburbs would be completely destroyed and nearly devoid of all life.
What is deadlier than the Tsar Bomba
However, the Soviet Union developed three AN602 physics packages at 101.5 megatons (Mt) and these are more powerful than the Tsar Bomba, which was downscaled to 51 Mt before being used RDS-220 Vanya.
What is the US strongest weapon
B83
B83 nuclear bomb
| B83 | |
|---|---|
| Used by | United States |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory |
| No. built | 650 |
Which God has most powerful weapon
Trishula – The trident of Shiva, stylized by some as used as a missile weapon and often included a crossed stabilizer to facilitate flight when thrown. Considered to be the most powerful weapon.
What is America’s strongest weapon
B83 nuclear bomb
| B83 | |
|---|---|
| Used by | United States |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory |
| No. built | 650 |
Why doesn t Japan have nukes
Since the bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, Japan has been a staunch upholder of antinuclear sentiments. Its postwar Constitution forbids the establishment of offensive military forces, and in 1967 it adopted the Three Non-Nuclear Principles, ruling out the production, possession, or introduction of nuclear weapons.