How did Iran develop nuclear weapons
Iran's nuclear program began as a result of the Cold War alliance between the United States and the Shah of Iran, Mohammad Reza Pahlavi, who emerged as an important US ally in the Persian Gulf. Under the Atoms for Peace program, Iran received basic nuclear research facilities from the United States.
What would happen if Iran got nukes
Iran's possession of nuclear weapons will create greater instability in the Middle East. An inadvertent or accidental nuclear exchange between Israel and Iran is a dangerous possibility.
When did Iran start its nuclear program
Iran's nuclear program was launched in the 1950s with the help of the United States. On 5 March 1957, a "proposed agreement for cooperation in research in the peaceful uses of atomic energy" was announced under the Eisenhower administration's Atoms for Peace program.
Has Iran signed the NPT
Iran is a party to the NPT since 1970 but was found in non-compliance with its NPT safeguards agreement, and the status of its nuclear program remains in dispute.
Why Iran can’t make nuclear weapons
But thanks to this nuclear deal, Iran must reduce its stockpile of uranium by 98%, and will keep its level of uranium enrichment at 3.67% — significantly below the enrichment level needed to create a bomb. Iran also needs tens of thousands of centrifuges to create highly enriched uranium for a bomb.
Is Iran allowed to develop nuclear weapons
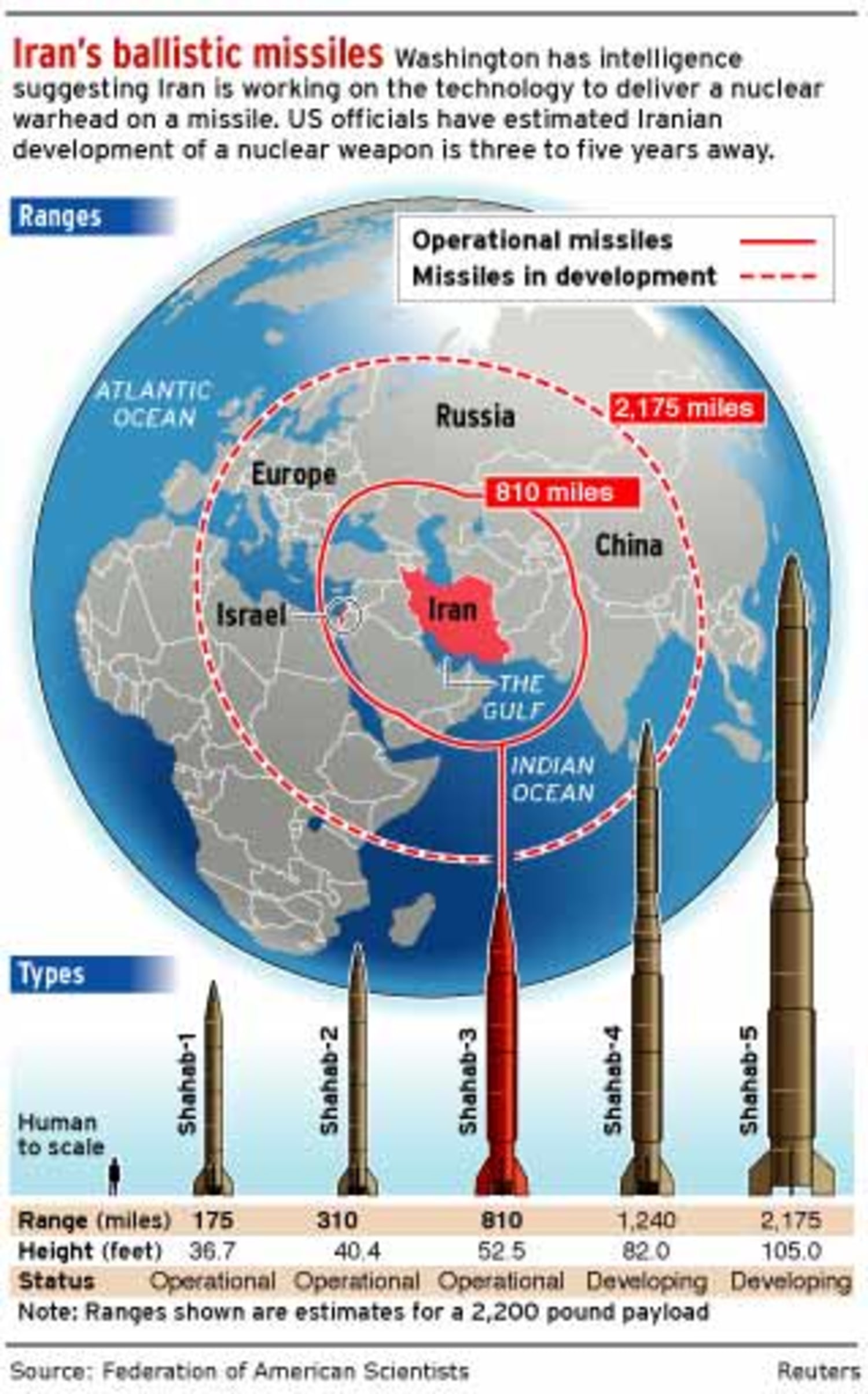
According to official U.S. assessments, Iran halted its nuclear weapons program in late 2003 and has not resumed it. This program's goal, according to U.S. officials, was to develop an implosion-style nuclear weapon for Iran's Shahab-3 ballistic missile.
How close is Iran to nuclear bomb
Summary. Iran's nuclear program has reached the point at which, within three to four weeks, Iran might be able to enrich enough uranium for five fission weapons.
Who negotiated Iran nuclear deal
Former US President Barak Obama, who played a key role in negotiations, was clear from the outset about the limited aims of the JCPOA. It was not designed to address other aspects of Iranian policy or behaviour; rather, its singular goal was to cut off all avenues for Iran to obtain a nuclear weapon.
Why does Iran want nuclear weapons
Likewise, Iranian policymakers certainly must believe that a nuclear weapon would provide them with enhanced deterrence against a U.S. attack, but the same goal could also be accomplished by the removal of U.S. and similar outside threats to Iran.
Who negotiated the Iran nuclear deal
Former US President Barak Obama, who played a key role in negotiations, was clear from the outset about the limited aims of the JCPOA. It was not designed to address other aspects of Iranian policy or behaviour; rather, its singular goal was to cut off all avenues for Iran to obtain a nuclear weapon.
Can Iran make nuclear weapons
Currently, Iran has a uranium stockpile to create 8 to ten nuclear bombs. But thanks to this nuclear deal, Iran must reduce its stockpile of uranium by 98%, and will keep its level of uranium enrichment at 3.67% — significantly below the enrichment level needed to create a bomb.
Why did Iran want to develop nuclear weapons
Likewise, Iranian policymakers certainly must believe that a nuclear weapon would provide them with enhanced deterrence against a U.S. attack, but the same goal could also be accomplished by the removal of U.S. and similar outside threats to Iran.
Who is allied with Iran
Syria. Syria and Iran are strategic allies. Syria is often called Iran's "closest ally", the Arab nationalism ideology of Syria's ruling Baath party notwithstanding.
Why is nuclear Iran a threat
A nuclear-armed Iran would likely further embolden Iran's aggressive foreign policy, including its deep ongoing involvement in Syria, its attacks against Israel via proxies including Hezbollah, Hamas and other terrorist groups, and its sponsorship of rebel insurgents in Yemen.
Was the Iranian nuclear deal good
Without the deal, any restrictions that block Tehran's path to a bomb would be gone and international monitoring of Iran's nuclear activities would be lost. There is no other realistic achievable alternative to prevent a nuclear-armed Iran.
How long would it take Iran to build a nuke
If Iran decided to rush to make a bomb without the deal in place, it would take them 2 to 3 months until they had enough weapon-ready uranium (or highly enriched uranium) to build their first nuclear weapon.
Who is Iran’s strongest ally
Syria. Syria and Iran are strategic allies. Syria is often called Iran's "closest ally", the Arab nationalism ideology of Syria's ruling Baath party notwithstanding.
Is Iran a Chinese ally
They have developed a friendly, economic and strategic relationship. In March 2021, Iran and China signed a 25-year cooperation agreement that will strengthen the relations between the two countries and that would include “political, strategic and economic” components.
Why is Iran so important in the world
It is a founding member of the United Nations, the ECO, the OIC, and the OPEC. It has large reserves of fossil fuels—including the second largest natural gas supply and the third-largest proven oil reserves. The country's rich cultural legacy is reflected in part by its 26 UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
Who is negotiating with Iran on nuclear
At the heart of negotiations with Iran were the five permanent members of the UN Security Council (China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States) and Germany—collectively known as the P5+1. The European Union also took part.
How strong is Iran’s military
Iranian Armed Forces are the largest in the Middle East in terms of active troops. Iran's military forces are made up of approximately 610,000 active-duty personnel plus 350,000 reserve and trained personnel that can be mobilized when needed, bringing the country's military manpower to about 960,000 total personnel.
Who is Iran’s biggest enemy
The biggest rivalry in the Arab–Iranian conflict is between Saudi Arabia and Iran, who have been waging a heavy proxy war against each other since the late 1970s.
Is Iran a Russian ally
Iran and Russia are strategic allies and form an axis in the Caucasus alongside Armenia. Iran and Russia are also military allies in the conflicts in Syria and Iraq and partners in Afghanistan and post-Soviet Central Asia. The Russian Federation is also the chief supplier of arms and weaponry to Iran.
What is Iran rich in
It is dominated by oil and gas production, although over 40 industries are directly involved in the Tehran Stock Exchange.
Is Iran rich in history
Iran is home to one of the world's oldest continuous major civilizations, with historical and urban settlements dating back to 4000 BC.