Who gets the money from IPO
When a company goes public, the company initially gets all of the money raised through the IPO. When the shares trade on a stock exchange after the IPO, the company does not get any of that money. That is money that is exchanged between investors through the buying and selling of shares on the exchange.
Does company get all the money from an IPO
While companies get to keep most of their IPO proceeds, a portion also goes to all investment banks, accountants, lawyers, and others who helped them with the IPO process, including valuing the company and setting an IPO cutoff price. According to PWC, underwriting fees alone eat up 3.5% to 7% of IPO proceeds.
Who buys IPO stocks
Instead, management, employees, friends and families of the company going public may be offered the chance to buy shares at the IPO price in addition to investment banks, hedge funds and institutions. High-net-worth clients may be rewarded with IPO shares from time to time as well.
How does a company receive money from IPO
All the trading that occurs on the stock market after the IPO is between investors; the company gets none of that money directly. The day of the IPO, when the money from big investors hits the corporate bank account, is the only cash the company gets from the IPO.
Who benefits from an IPO
An IPO allows a company to raise equity capital from public investors. The transition from a private to a public company can be an important time for private investors to fully realize gains from their investment as it typically includes a share premium for current private investors.
Who owns a company after an IPO
After the IPO, the primary investors will therefore control almost 60% of the firm's equity. The ownership stake of the original shareholders, who controlled 100% of the shares before the IPO, will consequently drop to 42.35% (= 1 − 0.5765) after the IPO.
How do investors benefit from IPO
By investing in an IPO, you can enter the 'ground floor' of a company with a high growth potential. An IPO may be your window to rapid profit in a short time period. It may also help grow your wealth in the long run. Suppose, you invest in a young company that sells disruptive technology.
How do investors make money from IPO
You become a shareholder of the firm if you take part in an IPO and purchase equity. As a shareholder, you have two options for financial gain: either you may sell your shares at a profit on the stock market, or the firm will pay you dividends on the shares you own.
What do companies do with their IPO money
The proceeds may be used to expand the business, fund research and development or pay off debt. Other avenues for raising capital, via venture capitalists, private investors or bank loans, may be too expensive. Going public in an IPO can provide companies with a huge amount of publicity.
What happens to CEO after IPO
Post-IPO, chief execs typically find themselves managing bigger headcounts, plus more complex demands from investors to streamline operations or grow into new markets. Skills which many typically don't possess, the researchers say.
How much do founders own after IPO
The list below shows founder ownership of 106 tech companies at IPO. The median level of ownership shown is 15% while the average is 21%. A few things to consider: -Businesses that tend to be less cash needy have higher levels of ownership for the founders.
What do companies do with the money from IPO
The proceeds may be used to expand the business, fund research and development or pay off debt. Other avenues for raising capital, via venture capitalists, private investors or bank loans, may be too expensive. Going public in an IPO can provide companies with a huge amount of publicity.
Why do companies go for IPO
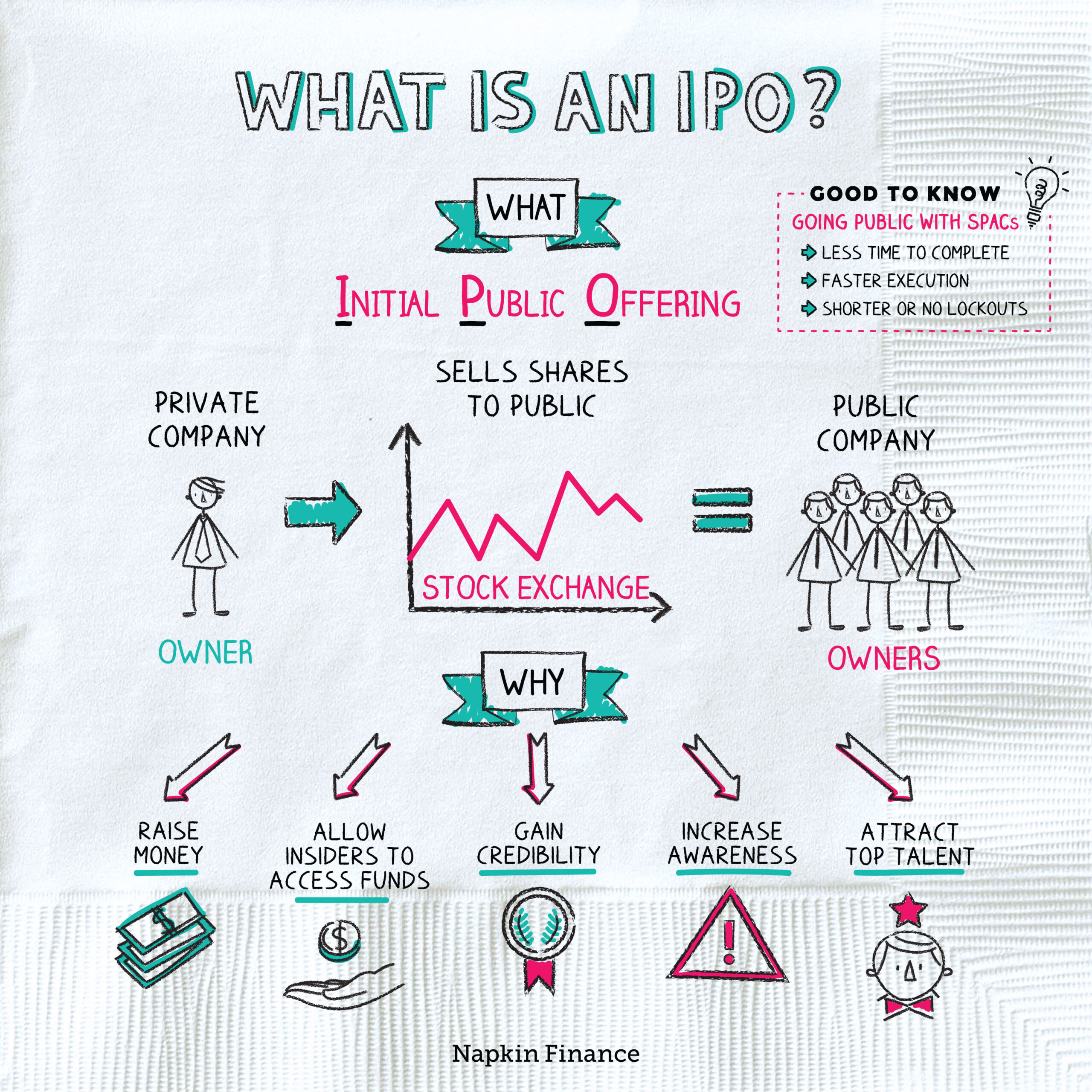
Companies decide to go public when they earn profits and capital returns and if the public demand for the company's share increases. This process is also known as Initial Public Offering or an IPO. In the initial days of a business, it is aided by promoter funds that include the entrepreneur's savings.
How does an IPO work for owners
When a private company first sells shares of stock to the public, this process is known as an initial public offering (IPO). In essence, an IPO means that a company's ownership is transitioning from private ownership to public ownership. For that reason, the IPO process is sometimes referred to as "going public."
What was the largest IPO of all time
Saudi Aramco
Saudi Aramco
The largest IPO of all time somewhat unsurprisingly goes to Saudi Arabian oil giant, Saudi Aramco.
How much does CEO earn at IPO
These individuals were independently wealthy before the IPO, but it is good to see a CEO pass up a big salary if they can and sets a tone for the entire company. $335k is the median for a very successful company. Keep in mind, the median salary of $335,280 is for the CEO of a SaaS company about to go public.
Do we get IPO money back
It usually takes 3 to 10 days to get IPO refunds after IPO allotments are done by the registrar of the IPO. It also depends on how you are getting the refunds.
Why do investors prefer IPO
An IPO is an opportunity to pick winning stocks and support at a competitive price in the shares of future industry leaders that provide valuable earnings by way of stock appreciation. Due to the reasonable price, one can buy multiple shares of the issuer company at an affordable price.
Why do investors buy IPO
By investing in an IPO, you can enter the 'ground floor' of a company with a high growth potential. An IPO may be your window to rapid profit in a short time period. It may also help grow your wealth in the long run. Suppose, you invest in a young company that sells disruptive technology.
What was the biggest IPO fail
10 Worst Failed IPOs in HistoryRobinhood. Robinhood's Initial Public Offering was deemed one of the worst IPOs ever for a company of its size, with shares falling as much as 10% within minutes of the opening of trading.Pets.com.Uber.SmileDirectClub.Root.Casper Sleep Inc.Etsy.TheGlobe.com.
Are most IPOs profitable
No, IPOs do not always have a profit. Many times a company is overvalued or valued incorrectly and its stock price falls after the IPO and never reaches the IPO value that investors paid for, therefore, not making any money but rather losing money.
How much did Mark Zuckerberg make from IPO
Zuckerberg sold 30.2 million shares for $1.15 billion during the offering. Most of the proceeds will be used to pay the taxes associated with exercising 60 million stock options. Facebook's $104.2 billion valuation crystallizes the fortunes of the company's three other co-founders.
What is the main reason why companies go public with an IPO
Going public refers to a private company's initial public offering (IPO), thus becoming a publicly-traded and owned entity. Businesses usually go public to raise capital in hopes of expanding. Additionally, venture capitalists may use IPOs as an exit strategy (a way of getting out of their investment in a company).
Why do companies go through an IPO
Companies want to go public for different reasons, depending on their circumstances. Most are looking to raise capital to fund expansion, pay debts, attract and retain talent, or monetise assets. A company may also want to list on a stock exchange to improve its public profile.
Why do companies want IPO
There are other reasons for a company to pursue an IPO, such as raising capital or boosting a company's public profile: Companies can raise additional capital by selling shares to the public. The proceeds may be used to expand the business, fund research and development or pay off debt.