Is 1 an identity element
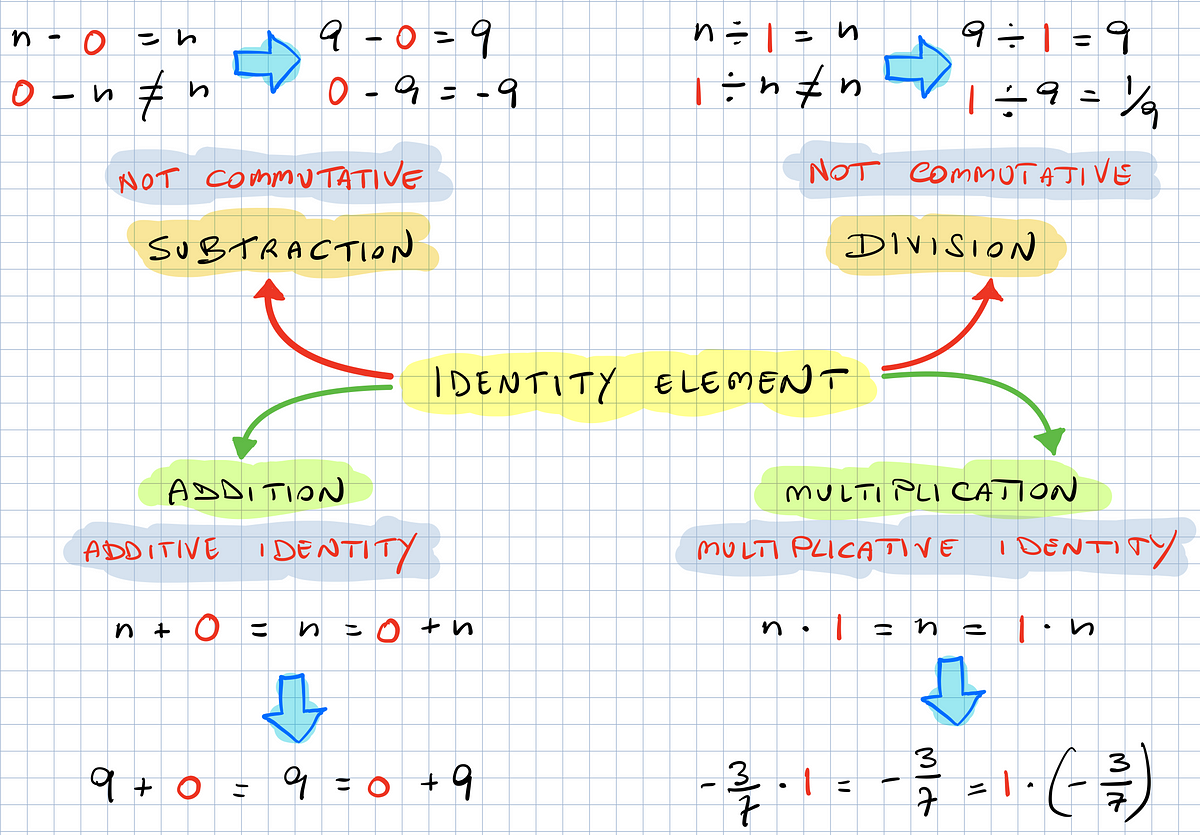
The two most familiar examples are 0, which when added to a number gives the number; and 1, which is an identity element for multiplication. The identity element is sometimes also called a neutral element; and sometimes shortened to simply the term identity.
Why is 1 an identity element of addition
It is False. 1 is the identity element for multiplication, because if you multiply any number by 1, the number doesn't change. Identity elements are specific to each operation (addition, multiplication, etc.). So while 1 is the identity element for multiplication, it is NOT the identity element for addition.
What is the identity property of 1
The identity property of 1 says that any number multiplied by 1 keeps its identity. In other words, any number multiplied by 1 stays the same. The reason the number stays the same is because multiplying by 1 means we have 1 copy of the number. For example, 32×1=32.
Why is 1 called the multiplicative identity
We get the same number as the result when we multiply it by 1. The number does not change, which means it keeps its identity, which is the reason for the name of the property. And, we can say that 1 is the multiplicative identity.
Is 1 the identity for integers
– 1 is multiplicative identity for integers, i.e., a × 1 = 1 × a = a for any integer a.
Is 0 an identity
“Zero” is called the identity element, (also known as additive identity) If we add any number with zero, the resulting number will be the same number. This is true for any real numbers, complex numbers and even for imaginary numbers.
Is identity element always 0 and 1
The identity will be either 0 or 1, depending on the operation that we are using. In addition and subtraction, the identity is 0. In multiplication and division, the identity is 1. That means that if 0 is added to or subtracted from n, then n remains the same.
Is 1 an identity matrix
An identity matrix is a given square matrix of any order which contains on its main diagonal elements with value of one, while the rest of the matrix elements are equal to zero.
Does identity matrix mean 1
In linear algebra, an identity matrix is a matrix of order nxn such that each main diagonal element is equal to 1, and the remaining elements of the matrix are equal to 0.
Why is 1 not a multiplicative identity of integers
The answer is TRUE……… Reason—-> 1 is the multiplicative identity for all numbers like integers , as if any integer is multiplied with 1, then the product is the number itself, but if multiplied with -1, then the sign of the number changes. So -1 is not the multiplicative identity for integers……….
Who invented 1
Hindu-Arabic numerals, set of 10 symbols—1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0—that represent numbers in the decimal number system. They originated in India in the 6th or 7th century and were introduced to Europe through the writings of Middle Eastern mathematicians, especially al-Khwarizmi and al-Kindi, about the 12th century.
Why is 1 an integer
An integer (pronounced IN-tuh-jer) is a whole number (not a fractional number) that can be positive, negative, or zero. Examples of integers are: -5, 1, 5, 8, 97, and 3,043.
Why is 1 not an integer
Is 1 an integer Yes, 1 is an integer. Integers are like whole numbers ( 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, … (and so on)), but they also include negative numbers … but still, no fractions allowed!
What is the identity property of 0 and 1
The number 0 has the additive identity property. On the other hand, a multiplicative identity is a number that when multiplied to any number gives the product as the number itself. The number 1 has the multiplicative identity property.
Why a 0 is not defined
The reason that the result of a division by zero is undefined is the fact that any attempt at a definition leads to a contradiction. a=r*b. r*0=a. (1) But r*0=0 for all numbers r, and so unless a=0 there is no solution of equation (1).
Is identity matrix always 1
The Identity Matrix is a Square Matrix in which each element of the main diagonal is 1 and each other element is 0. Also known as the Identity Matrix. Represents an Identity Matrix of degree n × n (or n) as I. This is sometimes referred to simply as I.
Is 1 the additive identity
Zero (0) is the additive identity and one (1) is the multiplicative identity for all the numbers such as whole numbers, natural numbers, integers, etc.
What matrix is a 1
The inverse of a square matrix A, denoted by A-1, is the matrix so that the product of A and A-1 is the Identity matrix. The identity matrix that results will be the same size as the matrix A.
What does a 1 mean in matrix
The inverse of a square matrix A, denoted by A-1, is the matrix so that the product of A and A-1 is the identity matrix. The identity matrix that results will be the same size as matrix A.
Is 0 an identity matrix
Although there is a zero matrix (additive identity) of every size, there is only a multiplicative identity for square matrices of size n-by-n, called I_n (with 1's on the main diagonal, and 0's elsewhere).
Is 1 the multiplicative identity for integers to or false
Hence, the multiplicative identity for all integers is 1.
Is 1 the multiplicative identity of integer True or false
As per integer rules we know that 1 is a multiplicative identity for integers. Therefore, the given statement -1 is not a multiplicative identity for integers is a true statement.
Who invented the numerals 1 to 9 and 0
For example, the Arabic numeral system we're all familiar with today is usually credited to two mathematicians from ancient India: Brahmagupta from the 6th century B.C. and Aryabhat from the 5th century B.C.
Who said 1×1 2
Terryology. In a 2015 interview with Rolling Stone, Howard explained that he had formulated his own language of logic, which he called Terryology, and which he was keeping secret until he had patented it. This logic language, he claimed, would be used to prove the statement "1 × 1 = 2". "How can it equal one" he said.
Is 1 an integer yes or no
An integer (pronounced IN-tuh-jer) is a whole number (not a fractional number) that can be positive, negative, or zero. Examples of integers are: -5, 1, 5, 8, 97, and 3,043. Examples of numbers that are not integers are: -1.43, 1 3/4, 3.14, .09, and 5,643.1.