What is the future of Japan’s economy
Japan's economy is expected to grow modestly as pent-up demand drives spending in the near term, and a relatively strong labor market maintains spending thereafter. The path of inflation will largely determine changes in monetary policy and therefore how quickly the economy can grow this year.
How can Japan fix its economy
The Economic Strategy Council judges that the economic revival of Japan would be impossible without reforming the current employment system of government employees, strongly implementing various institutional reforms including deregulation, improving the accounting methods in the public sector, fundamentally …
What will happen to Japan in the future
And Japan's future will have lessons for the rest of us. In the age of artificial intelligence, fewer workers could drive innovation; Japan's aged farmers may be replaced by intelligent robots. Large parts of the country could return to the wild. Will Japan gradually fade into irrelevance, or re-invent itself
Why is Japan GDP not growing
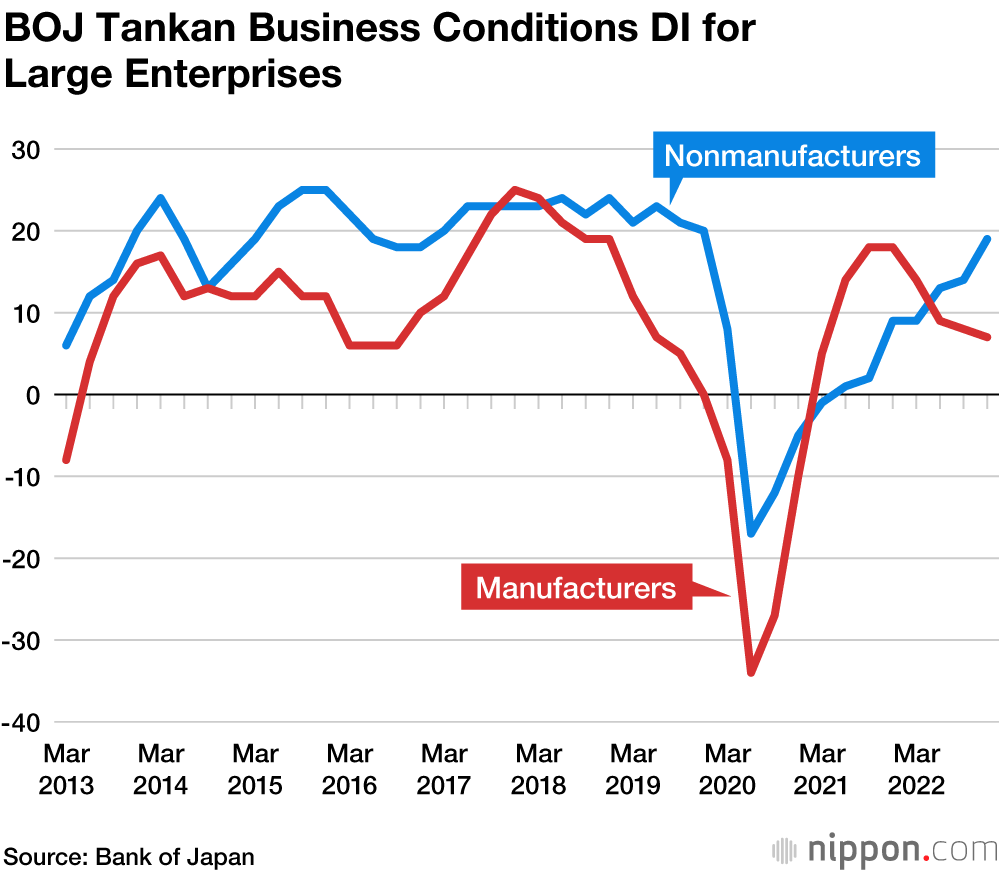
Japan's economy is being buffeted by slowing overseas demand due to deteriorating global growth, resulting in a record trade deficit and the largest factory output contraction in eight months in January.
Is Japan’s economy expected to grow
Economists expect the economy to continue to grow, albeit at a slower pace, in the second quarter. The latest figures showed Japan avoided a technical recession at the end of 2022, but it continues to alternate between growth and contraction.
Will Japan’s economy grow
The upside surprise for Japan's economic growth comes as stocks remain in focus after recently notching new three-decade highs thanks to a weak yen and plans for structural reforms. Factory activity in the economy expanded for the first time since October 2022, a Purchasing Managers' Index from last week showed.
Why is Japan’s economy weak
Supply chain issues, rising labor costs, and political issues have highlighted problems with Japan's reliance on China as a base for its manufacturing investments. With a low birthrate and aging population, Japan's social security system is under strain and is suffering from labor shortages.
What is Japan economic weakness
WEAKNESSES. Rapidly ageing population. Reduction of the workforce and low immigration contribution, increasing share of precarious workers. Difficulty in fiscal consolidation and reversal of deflationary pressures. Low growth potential, low productivity of SMEs.
Will Japan start growing again
Japan is expected to grow at 1.8 percent in 2023, which is a slight upgrade from 1.6 percent in the October World Economic Outlook. As the government has relaxed COVID-19 related restrictions and reopened borders, growth has been boosted by pent-up demand, supply chain improvements and policy support.
Is Japan’s economy weak
The economy contracted 1.2 percent as consumers and businesses were hit with rising import prices. Japan's economy, the world's third largest, unexpectedly shrank in the three-month period from July to September, as a weak yen and high inflation eroded Japanese consumers' buying power and sapped businesses' strength.
Why did Japan’s economy collapse
By the late 1980s, the Japanese economy experienced an asset price bubble of a massive scale. The bubble was caused by the excessive loan growth quotas dictated on the banks by Japan's central bank, the Bank of Japan, through a policy mechanism known as the "window guidance".
Is Japan financially stable
Japan is fundamentally stable socially, politically, and economically, with an ethnically homogeneous population of 126 million.
Why did Japan’s economy slow
Japan's "Lost Decade" was a period that lasted from about 1991 to 2001 that saw a significant slowdown in Japan's previously bustling economy. The economic slowdown was caused, in part by the Bank of Japan (BOJ) hiking interest rates to cool down the real estate market.
Is the Japanese economy getting better
The upside surprise for Japan's economic growth comes as stocks remain in focus after recently notching new three-decade highs thanks to a weak yen and plans for structural reforms. Factory activity in the economy expanded for the first time since October 2022, a Purchasing Managers' Index from last week showed.
What is the biggest problem in Japan
TOKYO — With the world's oldest population, rapidly declining births, gargantuan public debt and increasingly damaging natural disasters fueled by climate change, Japan faces deep-rooted challenges that the longstanding governing party has failed to tackle.
Why did Japanese economy collapse
In the early 1990s, as it became apparent that the bubble was about to burst, the Japanese Financial Ministry raised interest rates, and ultimately the stock market crashed and a debt crisis began, halting economic growth and leading to what is now known as the Lost Decade.
Is Japan already living in the future
The Japanese have embraced technology like no other nation on the planet. From robots to super-fast bullet trains to impressive vending machines, these citizens of the land of the Rising Sun appear to live decades or even hundreds of years in the future.
Is Japan’s economy good or bad
Japan generally runs an annual trade surplus and has a considerable net international investment surplus. Japan has the third-largest financial assets in the world, valued at $12 trillion, or 8.6% of the global GDP total as of 2020. As of 2022, 47 of the Fortune Global 500 companies are based in Japan.
Why is Japan in so much debt
A flurry of big spending packages and ballooning social welfare costs for a rapidly ageing population have left Japan with a debt pile 263% the size of its economy – double the ratio for the United States and the highest among major economies.
Why does Japan have a weak economy
Supply chain issues, rising labor costs, and political issues have highlighted problems with Japan's reliance on China as a base for its manufacturing investments. With a low birthrate and aging population, Japan's social security system is under strain and is suffering from labor shortages.
Why Japan is not growing
It had to rearrange its production system and other economic institutions to cope with globalization to reduce its reliance on external demand. Japan's population structure was shifting and becoming increasingly elderly. Aging meant slower growth of the labor force.
Why did Japan’s economy crash
Key Takeaways. Japan's "Lost Decade" was a period that lasted from about 1991 to 2001 that saw a significant slowdown in Japan's previously bustling economy. The economic slowdown was caused, in part by the Bank of Japan (BOJ) hiking interest rates to cool down the real estate market.
Why is Japan’s economy so strong
Manufacturing has been the most remarkable, and internationally renowned, feature of Japan's economic growth. Today, Japan is a world leader in the manufacture of electrical appliances and electronics, automobiles, ships, machine tools, optical and precision equipment, machinery and chemicals.
Is Japan the most futuristic country
Japan, South Korea, and the United States top the list, followed by Germany, China, Singapore, Sweden, Switzerland, the United Kingdom, and Finland.
Is Japan’s economy improving
Japan's economy grew an annualized 2.7% in the first quarter of the year, expanding further than earlier estimates of 1.6% made last month, government data showed Thursday.